Streamline Maintenance with Maintainly Work Order Checklists
Maintainly has updated a key aspect of how maintenance checklists are created and performed in work orders.
Key changes Include:
Three types of checklists can be now be created:
Task templates can have their own checklist to be repeated each time that task template is used;
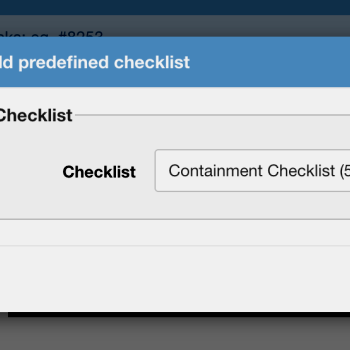
Predefined checklists can be created in advance & added to any task, at any time;
Ad-hoc checklists can be added on-the-fly to any task, at any time.
Each of these checklist types is explored in more detail below.
Adding a Checklist to a Task
Checklists on a task template will appear automatically in the tasks every time the task template is used.
But, predefined checklists, as well as ad-hoc checklists, can be added to any task (preventative or unscheduled) at any time.
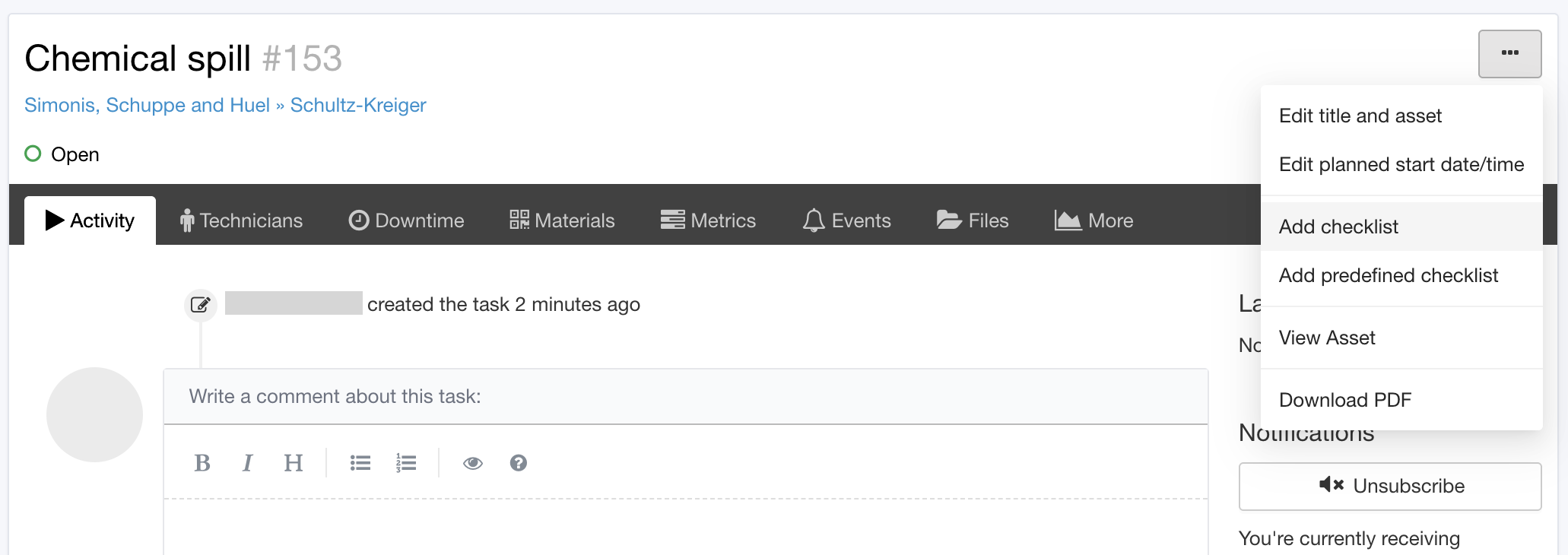
Types of Checklists in Maintainly
1. Task Template Checklists
Perfect for recurring work like preventive maintenance, these checklists can be built into your existing task templates. They create standardized procedures that carry over each time the template is used, ensuring consistent quality across all similar maintenance tasks.
Example: Weekly room check at a small hotel
At a medium-sized hotel, the housekeeping and maintenance teams perform a weekly guest room maintenance check to ensure rooms remain in top condition. By embedding a standardized checklist into the hotel’s weekly preventative maintenance task template, the maintenance team ensures consistency and high quality in every room inspection. The checklist might look something like this:
Check HVAC air filters for condition (replace if necessary)
Test the thermostat for proper operation
Check for unusual noises or airflow issues
Inspect sinks, showers, and toilets for leaks or slow drains
Test water pressure and temperature
Ensure the toilet flushes properly without any issues
Examine furniture (beds, chairs, desks) for damage or instability
Check the condition of curtains or blinds, ensuring smooth operation
Inspect mirrors, picture frames, and decorative items for cracks or alignment
Test the television, remote, and cable functionality
Confirm Wi-Fi connection strength and test guest room internet devices
Look for stains or damage on walls, ceilings, or carpets
Test door locks, including electronic keycard systems, for smooth operation
2. Predefined Checklists
Created and approved in advance, these checklists can then be inserted into any active work order. They contain fixed steps that technicians must follow, ensuring procedures are performed exactly as specified without unauthorized modifications.
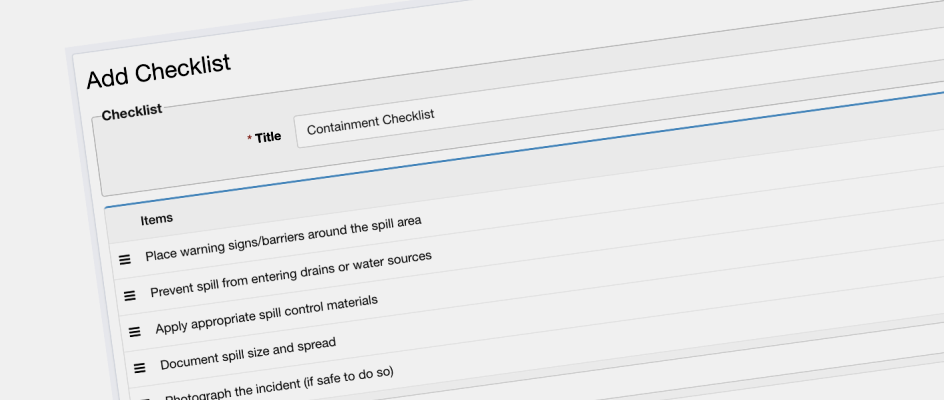
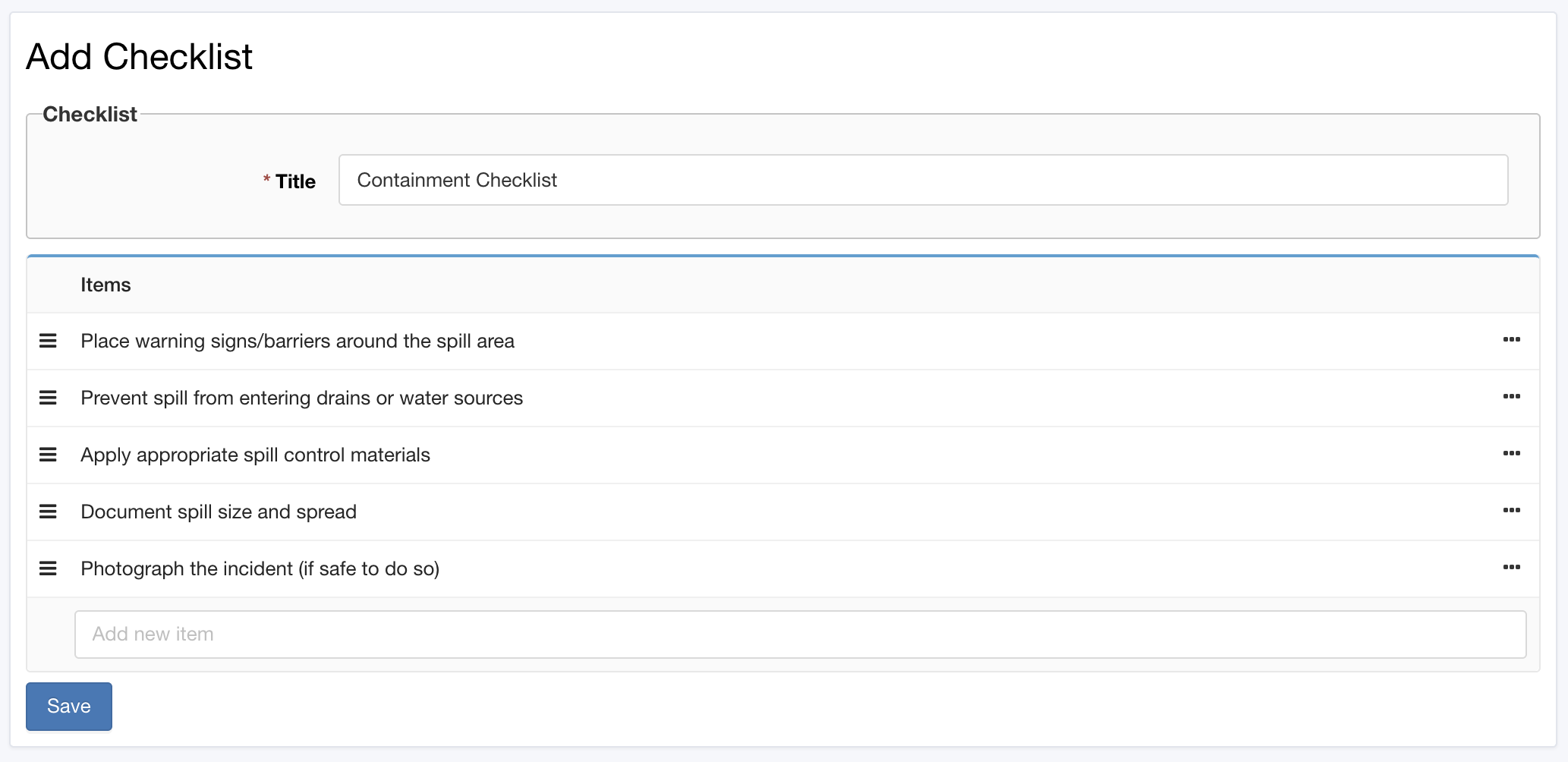 Example: Chemical Spill Response in a Manufacturing Facility
Example: Chemical Spill Response in a Manufacturing Facility
Imagine a chemical spill occurs in your facility. In this high-stress situation, skipping crucial safety steps could be dangerous. A series of predefined "Chemical Spill Response" checklists ensures proper handling every time. A typical checklist might look something like this:
Initial Response Checklist
Clear the area of all personnel
Identify the spilled chemical using storage labels
Check Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for specific handling requirements
Don appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Secure and ventilate the area
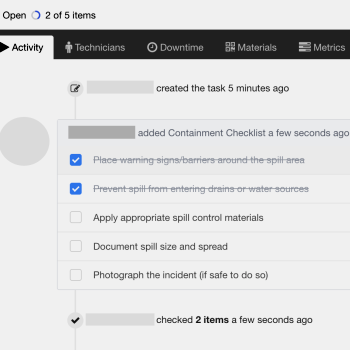
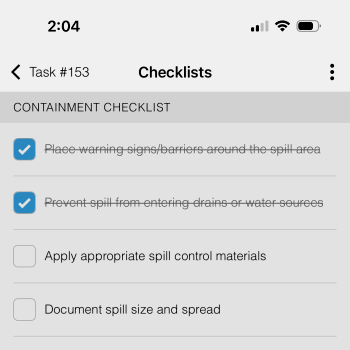
Containment Checklist:
Place warning signs/barriers around the spill area
Prevent spill from entering drains or water sources
Apply appropriate spill control materials
Document spill size and spread
Photograph the incident (if safe)
Reporting Checklist:
Notify facility supervisor
Contact emergency response team if needed
Record incident details in Maintainly
Document any injuries or exposure
File necessary regulatory reports
3. Ad-hoc Checklists
These flexible checklists can be created by any user during task execution. They're ideal for tracking progress on unique jobs or capturing additional steps that arise during maintenance work.
An ad-hoc checklist empowers technicians to handle dynamic situations efficiently while maintaining a clear record of work performed.
Example: Corrective Maintenance Task at Manufacturing Plant
A maintenance technician is dispatched to repair a malfunctioning conveyor belt in a manufacturing plant. The initial work order specifies a few basic steps, such as inspecting the belt, replacing worn components, and testing the system. However, during the inspection, the technician discovers additional, related issues that require attention beyond the original scope.
During the inspection, the maintenance technician notices that:
The motor mount is loose.
A misaligned pulley is causing additional strain on the belt.
These issues are not listed in the original work order checklist but must be addressed to ensure the conveyor operates properly.
Using Maintainly mobile CMMS on their tablet, the technician creates an ad-hoc checklist directly within the existing task. The maintenance technician adds the following items:
Tighten motor mount bolts
Realign the pulley
Lubricate all moving components
Understanding Maintenance Checklists
Maintenance checklists are essential tools that guide technicians through required steps, inspections, and tasks within a work order. By providing a clear, structured approach to maintenance activities, these checklists ensure work is performed consistently, accurately, and in compliance with standards.
In complex scenarios, multiple checklists can be added to a single work order to ensure comprehensive task completion. For example, in the chemical spill scenario described above, you might need to add:
The initial "Chemical Spill Response" checklist
A "PPE Inspection" checklist
An "Environmental Compliance" checklist
A "Post-Incident Area Restoration" checklist
Each checklist serves its specific purpose, so could be used independently, but can also work together to ensure all aspects of the incident are properly managed. This flexibility allows you to build a complete response that matches the complexity of the situation, rather than trying to fit everything into a single, overwhelming checklist.
The ability to combine multiple predefined checklists helps maintain clarity and organization while ensuring nothing is overlooked. Users can add relevant checklists (predefined or ad hoc) as the situation develops or changes, or requirements become clear.
Checklists create a detailed record of maintenance activities by documenting exactly what steps were performed, when they were completed, and who completed them. This systematic documentation generates a clear audit trail that proves required procedures were followed, safety protocols were observed, and maintenance standards were met. When integrated into a maintenance management system, these completed checklists become valuable historical records that can be easily referenced during audits, inspections, or compliance reviews, providing verifiable evidence of proper maintenance execution.
Key Benfits of Maintenance Checklists
Process Consistency
Consistency forms the foundation of effective maintenance operations. By providing standardized procedures, checklists ensure that work is performed the same way regardless of who completes it or when it's done. This standardization is particularly valuable across different shifts and locations, making it easier to train new staff and maintain quality standards across the organization. When every technician follows the same proven steps, the guesswork is eliminated and reliability improves.
Work Accuracy
Accuracy is enhanced through the systematic approach that checklists provide. Complex tasks become more manageable when broken down into clear, sequential steps that can be verified as they're completed. This methodical approach reduces errors by preventing steps from being missed or performed out of sequence. It also creates a verifiable record of completed work, helping technicians maintain focus even during routine tasks and ensuring proper documentation of all maintenance activities.
Compliance
Compliance is perhaps the most critical aspect in regulated industries. Checklists create a clear audit trail of maintenance activities, providing evidence that required procedures were followed correctly. This documentation is invaluable for meeting regulatory requirements, supporting certification needs, and maintaining quality standards. By tracking and verifying mandatory maintenance tasks, checklists help organizations demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory compliance.
Together, these three elements transform checklists from simple task lists into powerful tools for maintenance excellence. They provide the structure needed for consistent, high-quality work while remaining flexible enough to adapt to various maintenance scenarios. This combination of structure and flexibility ultimately leads to improved efficiency, reduced risks, and better maintenance outcomes.