Time-based preventative maintenance management explained
What is Preventative Maintenance?
Preventative maintenance is a proactive approach to equipment and system care designed to prevent failures and extend the lifespan of assets. This maintenance strategy involves regular inspections, servicing, and repairs based on a schedule rather than waiting for equipment to fail. The goal is to identify and address potential issues before they become serious problems, thereby reducing downtime, improving safety, and minimizing costly emergency repairs.
Preventative maintenance can include tasks like cleaning, lubricating, adjusting, and replacing parts, as well as monitoring performance indicators to ensure everything is functioning optimally.
This approach is widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and facility management, as it enhances operational efficiency and reliability. By adhering to a preventative maintenance schedule, organizations can better manage their resources, avoid unexpected breakdowns, and optimize the use of their equipment. Over time, this results in lower total maintenance costs and increased productivity, as equipment remains in good working condition and is less likely to experience catastrophic failures.
Time-based maintenance management refers to a maintenance strategy that involves performing maintenance tasks based on predetermined time intervals or schedules. This approach assumes that assets will require maintenance at regular intervals to prevent failures, ensure reliability, and extend each asset's useful life. Time-based maintenance is typically used for assets that experience predictable wear and degradation over time.
The time-based maintenance management process involves several key steps:
Asset Assessment
The first step is to assess and classify assets based on their criticality and maintenance requirements. Criticality refers to the asset's impact on business operations and the consequences of failure. This assessment helps prioritize maintenance efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Maintenance Planning
Once assets are assessed, maintenance plans are developed for each asset. These plans outline the specific maintenance tasks to be performed, their frequency, and the resources required. The plans may include activities such as inspections, lubrication, cleaning, component replacements, or system overhauls.
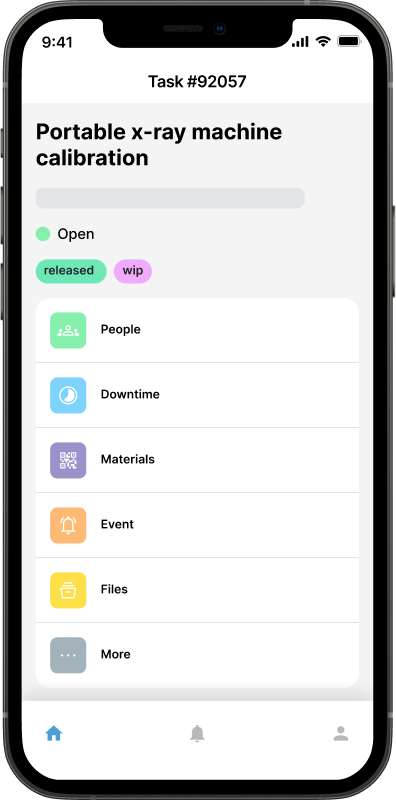
Work Order Generation
Work orders are created to initiate maintenance tasks. A work order typically includes details such as asset identification, description of the maintenance task, required materials or parts, estimated labor hours, and any special instructions or safety precautions.
Work Order Scheduling
The generated work orders are then scheduled based on the maintenance plans and available resources. The scheduling process takes into account factors such as equipment availability, technician availability, and the impact of maintenance activities on production or operational schedules.
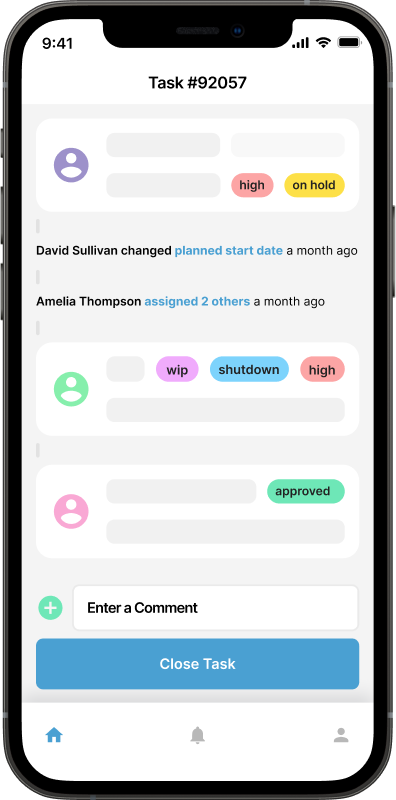
Execution and Completion
Once a work order is scheduled, the maintenance tasks are performed by qualified technicians. They follow the instructions outlined in the work order, use the necessary tools and materials, and adhere to safety protocols. After completing the maintenance tasks, technicians update the work order with relevant information, including any observations, measurements, or repairs made.
Data Capture and Documentation
Accurate data capture is essential for time-based maintenance management. Technicians record maintenance activities, including task completion times, materials used, and any findings during the maintenance process. This data provides a historical record of maintenance activities and helps in analyzing asset performance and identifying patterns or trends.
Performance Analysis
The captured data is analyzed to assess asset performance and the effectiveness of the time-based maintenance strategy. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as asset downtime, mean time between failures (MTBF), and maintenance costs are evaluated to identify areas for improvement and optimization. This analysis helps in refining maintenance plans, adjusting maintenance intervals, or identifying potential asset reliability issues.
CMMS for Continuous Improvement
Time-based maintenance management is an iterative process that requires continuous improvement. By leveraging a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), organizations can efficiently track and analyze the performance of their maintenance activities. Based on this performance analysis, adjustments can be made to maintenance plans, schedules, or strategies. The data and insights gathered through the CMMS help in learning from previous maintenance activities, allowing organizations to optimize future tasks and increase the overall efficiency of their maintenance program.
Implementing a time-based maintenance management approach, supported by a CMMS, enables organizations to proactively maintain assets, reduce the risk of unexpected failures, and ensure the reliability and longevity of their equipment. This integration allows for better resource planning, minimizes downtime, improves safety, and enhances overall operational efficiency by ensuring that maintenance tasks are performed consistently and effectively.