Managing a Spare Parts Warehouse: Essential Components and Best Practices

Effectively managing a spare parts warehouse is crucial to maintaining the smooth operation of industrial facilities, manufacturing plants, or any business reliant on machinery. Having a well-organized system ensures parts are easily accessible, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
In this guide, we'll discuss the essential components and methods of structuring and managing a spare parts warehouse, with a focus on using coding systems, QR labels, and shelving strategies.
Key Components of a Spare Parts Warehouse
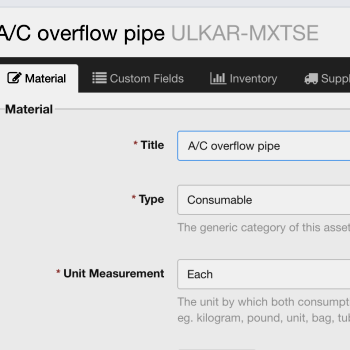
Inventory Management System The foundation of a well-managed warehouse is a robust inventory management system, typically integrated with a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System). This software helps track spare parts, manage reorders, and generate reports.
Random Coding Systems Rather than categorizing parts by type or usage alone, many modern warehouses use random coding systems. In this system, each part is assigned a random location code, which may not follow a logical pattern based on part type but is managed through software for efficient retrieval. This approach maximizes storage space and flexibility.
CMMS should assign unique codes to each part to streamline storage, retrieval, and reporting processes. Using a unique key in an inventory management system is imperative for many reasons, including:
Data Integrity: A unique key ensures that every inventory item is uniquely identifiable in the system. This prevents duplicates and ensures that the correct data is associated with the correct item.
Efficient Search and Tracking: Having a unique identifier allows for quick and accurate search, retrieval, and tracking of items in the inventory. This is crucial for tasks like order processing, restocking, and audits.
System Relationships: In many systems, inventory data is linked to other data sets, such as sales, suppliers, or locations. A unique key allows these relationships to be properly managed without confusion or mislinking records.
Scalability: As an inventory system grows, a unique key system allows for more efficient management and scaling without issues caused by duplication or conflicting data.
Compliance and Reporting: In industries where traceability is critical (e.g., pharmaceuticals, aerospace), unique keys are often required for compliance and regulatory purposes, ensuring items can be tracked from origin to sale.
Effectively implementing such a system results in some important advantages, including:
Increased storage density.
Flexibility to adapt to changes in part quantities.
Simplifies warehouse expansion without reorganizing entire sections.
QR Labels for Identification Implementing QR labels on spare parts enhances traceability and simplifies the management process. Each QR label can be linked to the item’s specific data in your inventory system, including part number, location, supplier information, and reorder status.
Benefits of implementing spare part QR labels, include:
Easy Scanning: Using a mobile device or barcode scanner, employees can instantly retrieve detailed information about a part.
Fast Tracking of Stock Levels: Scanning items as they are used or added helps maintain accurate stock counts.
Improved Workflow: Technicians can scan QR codes during maintenance tasks to verify they have the correct part and update stock levels directly, and immediately, in the CMMS.
Shelving Systems Based on Size and Weight A well-organized shelving system ensures that items are stored appropriately according to their size, weight, and handling requirements. Consider the following when designing your warehouse layout:
Heavy-Duty Shelving for Large Parts: Store heavy or bulky items, such as motors or large machine components, on lower, more accessible shelves. This reduces the need for equipment (like forklifts) to access them and minimizes the risk of injury from handling heavy parts.
Small Parts Bins: Use bins for smaller parts, such as bolts, gaskets, or fasteners. Label these bins with QR codes and organize them by random code, leveraging your software system for efficient retrieval.
Vertical Shelving for Space Optimization: Make use of vertical storage space, especially for lighter parts. Mobile shelving units or mezzanine levels can further optimize space.
Structuring the Warehouse

When structuring your warehouse, consider dividing it into specific zones based on material type or handling requirements. For example:
Critical Spare Parts Zone: Reserve specific shelves for high-demand or critical spare parts that must always be easily accessible.
Non-Critical Parts Zone: Store parts that are rarely used in less accessible areas, such as higher shelving units.
Bulk Storage Area: For larger or irregularly shaped items, designate a section of the warehouse with wider aisles for easier manoeuvring of forklifts or lifting equipment.
Thoughtful design that takes into account factors like the weight of items, positioning above shoulder height, and similar considerations can significantly reduce the risk of injury to technicians and warehouse staff.
Optimizing Workflow in the Warehouse
The warehouse layout should support efficient workflows for technicians and warehouse staff. Consider the following strategies:
Shorten Retrieval Times: Store frequently used parts in locations that are easy to access. Use your CMMS data to determine which parts are used most often and keep these near the front or in easily accessible areas.
When using Maintainly's part kits feature in preventative maintenance task templates, it can be beneficial to pre-assemble part kits in advance. This allows technicians to retrieve the kits quickly without needing to pick individual items from the warehouse. Alternatively, ensuring that parts included in these kits are stored close to one another can also streamline the retrieval process and improve efficiency.
Organized Picking Routes: For large warehouses, develop logical picking routes that avoid unnecessary walking and time wastage.
Designate Receiving and Inspection Areas: Clearly mark areas for receiving new stock, conducting inspections, and applying QR labels. A smooth intake process ensures new parts are quickly entered into the system and placed in their proper storage locations.
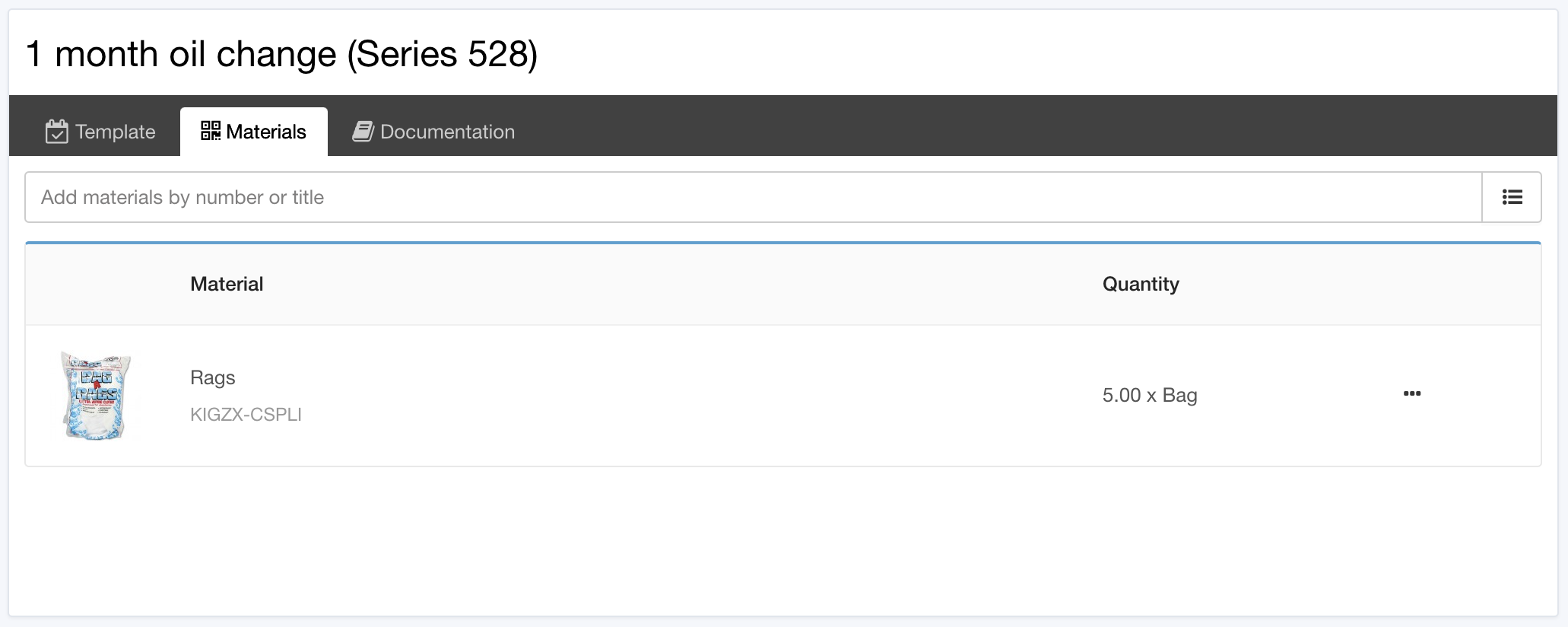 Using QR Labels with a CMMS Mobile App
Using QR Labels with a CMMS Mobile App
The ability to print and apply QR labels and scan them with a mobile app enhances the functionality of your CMMS and the efficiency of your maintenance team. Here's how the process works:
Label Creation and Application: After a new part is received and inspected, print a QR code label using your inventory system. Affix the label to the part or its bin.
Mobile App Integration: When technicians use a part for a task, they can scan the QR code using a mobile device. The system will automatically update the inventory, removing the used part from stock and notifying the warehouse team if levels are running low.
Streamlined Reordering: When stock reaches a predetermined minimum, the system can trigger an automatic reorder request to suppliers, ensuring that critical parts are always available.
Conclusion
Managing a spare parts warehouse efficiently requires a combination of smart technology and thoughtful organization. By implementing a random coding system, using QR labels, and designing shelving that accounts for the size and weight of materials, you can create a system that minimizes downtime, reduces stock discrepancies, and ensures smooth operations. Integrated with CMMS software, these strategies enable real-time tracking of inventory levels and seamless management of maintenance tasks, improving overall warehouse efficiency. Try Maintainly for free for 14 days.
Further Reading

What is CMMS?
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software solution that streamlines and automates maintenance management processes, including work orders, preventive maintenance, asset tracking, and inventory management, to optimize the efficiency and performance of organizational assets. But let's dig into the details...
Read more →